The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
- The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
- Access and Benefit-Sharing
- Convention on Biological Diversity
- Illegal Plant Trade Coalition
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
- The Sustainable Development Goals
- International Agenda for Botanic Gardens
 The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation (GSPC) is now in a new, third phase that is fully aligned to the 23 targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF). This new phase is currently being implemented (2024-2030) and follows the success of phase II, which operated between 2010 and 2020. The GSPC continues to highlight the importance of plants and the ecosystem services they provide for all life on earth, and ensures that plants get the conservation action they need and deserve as part of the broader Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and KMGBF.
The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation (GSPC) is now in a new, third phase that is fully aligned to the 23 targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF). This new phase is currently being implemented (2024-2030) and follows the success of phase II, which operated between 2010 and 2020. The GSPC continues to highlight the importance of plants and the ecosystem services they provide for all life on earth, and ensures that plants get the conservation action they need and deserve as part of the broader Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and KMGBF.
The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation 2020-2030 was formally adopted at the Convention on Biological Diversity CoP16, hosted in Cali Colombia in October 2024. The full text can be downloaded from the CBD website (Decision 16/20) This will be implemented from 2024-2030.
A summary document of the GSPC 2020-2030 is now published. This document is a concise summary of the new GSPC Complementary Actions and the rationales behind each of the new Actions. All gardens can be involved with the GSPC and many existing garden initiatives and work supports the GSPC. The summary document can be used as a tool to map existing institutional strategies to the GSPC and identify which Actions align with existing work within your organisation. It can also be used to identify priority Actions for individuals and organisations, within which goals can be set.
The Voluntary Complementary Actions
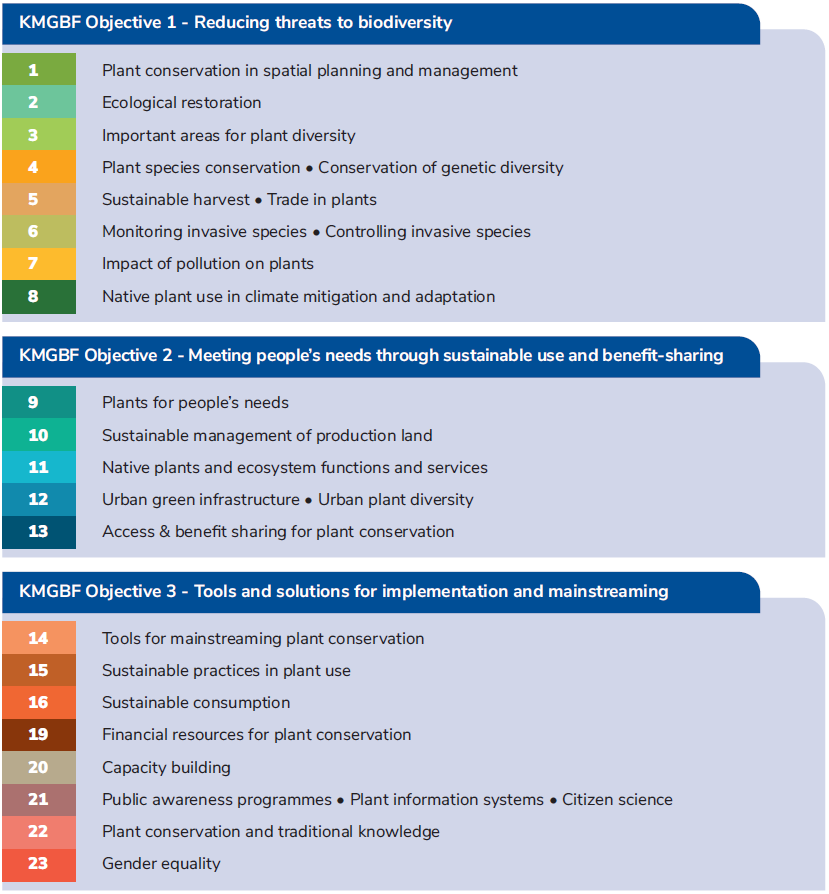
The Global Strategy for Plant Conservation 2020-2030 has 41 Voluntary Complementary Actions related to 21 of the KMGBF targets. The table below gives the summary titles and headings for each GSPC Action. Each number of a GSPC Action is equivalent to the number used for the relevant KMGBF target. Some KMGBF targets have only one relevant GSPC Action while other will have multiple GSPC Actions or Subactions. Two KMGBF targets have no particular plant conservation actions (17 and 18) defined for them, and therefore are not included in the GSPC Action tables.
Through this alignment of GSPC Actions to KMGBF Targets they are clearly identifiable as components, sub-targets or milestones towards the biodiversity targets and therefore easily integrated into NBSAPs, national or regional plant conservation action plans and botanic garden master plans. Therefore, the Voluntary Complementary Actions or plant actions provide the framework for the plant conservation community to take action for the world’s plant diversity.
Table 1: GSPC Global Strategy for Plant Conservation Action Headlines.
If you would like to get involved, please email policy@bgci.org and sign up to BGCI’s Cultivate Newsletter to be kept up to date with news.
A Post-2020 GSPC
The Voluntary Complementary Actions were developed through rigorous and broad consultation with international stakeholders. More information on the process of preparing this is available in BG Journal Vol 21 (1 ).
Before formal adoption in 2024 the proposed actions werepresented at SBSTTA 25, in Kenya 2023 (Document – SBSTTA 25-inf-4) . These actions were then recommended (CBD/SBSTTA/25/CRP.1) for adoption at the next Conference of the Parties (COP16). An information document (CBD/COP/16/INF/34) on possible indicators and a draft reporting template were also prepared ahead of CoP16 (by the GPPC) to support the GSPC discussions and debates at CoP16.
Founding of the GSPC
The original Global Strategy for Plant Conservation was developed in the early 2000’s and over the past 20 years has seen incredible success in providing a programmatic focus for the world’s plant conservation activities. This original strategy grew out of the CBD and has been fed into government policy around the world. For more information on GSPC activities from the beginning, follow this link or listen to episodes one and two of the Understory Podcast (2024) which provide an overview of the GSPC.
In 2010, as part of the 10th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the CBD, an updated GSPC, for the period 2010-2020 was adopted. This updated GSPC included 16 targets for plant conservation to be achieved by 2020. A review of progress in the implementation of this phase of the GSPC was carried out in 2020 and published by the CBD Secretariat in the Plant Conservation Report 2020.
Learn more about the GSPC from our Moodle module: Introduction to International Environmental Policies
Further details about the 2010-2020 GSPC are available on the GSPC toolkit.
BGjournal
Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
Roots
Associated resources
GSPC Summary Document
GPPC Climate Brief 2025
Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
A Guide to the Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
Plant Conservation and the Sustainable Development Goals
GSPC Flyer
Estrategia Mundial para la Conservación de las Especies Vegetales
Una Guía para la Estrategia Mundial para la Conservación de las Especies Vegetales
Stratégie Mondiale pour la Conservation des Plantes
Guide Pratique de la Stratégie Mondiale pour la Conservationdes Plantes
全球植物保护战略 《全球植物保护战略》指南
The Global Partnership for Plant Conservation
BGCI hosts the secretariat for The Global Partnership for Plant Conservation. The GPPC is made up of botanic and University gardens, arboreta, plant conservation NGO’s (such as Plantlife ) and other plant conservation stakeholders. The GPPC are pivotal in the development, implementation and reporting of the GSPC and the new complementary actions. The partnership supports capacity building, finding innovative ways to implement the targets and mobilizes actions at different levels to achieve the GSPC.
The Global partnership for Plant Conservation was launched in 2004 to support the activities of the GSPC. It now includes 70 members, including 21 international organizations and 47 national organizations representing 21 countries.
With the renewal of the GSPC and the complementary actions, the GPPC is seeking new members. If your organization would like to get involved please email policy@bgci.org.
Share





